In battery classification, there are two types based on battery rechargeability, i.e., rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries. There are many differences between the two besides the charging capabilities. For example, rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries differ in electrolyte composition, discharge characteristics, etc.
This article will highlight the differences between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries. We will start with the working principles of both batteries and then highlight their fundamental differences.
Working Mechanism of Rechargeable and Non-Rechargeable Batteries
Rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries perform electrochemical reactions to generate electricity. However, the working mechanisms of both battery types differ.
Working Principle of Rechargeable Battery
A rechargeable battery, also known as a secondary cell, uses reversible cell reactions, which allow it to revive its electrical potential when exposed to electric current.
During the discharge process, the battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy through the redox (reduction-oxidation) reaction. The electrons move from the anode to the battery’s cathode via an external circuit and power that circuit. In addition, the ions flow via the electrolyte to balance the charge and complete the circuit.
During the charging process, the above process is reversed. The external electrical source applies voltage and moves electrons from the cathode to the adobe. This reverses the battery’s chemical composition and makes it charged like before.
This way, a typical rechargeable battery discharges and charges frequently.
Working Principle of Non-Rechargeable Battery
Non-rechargeable batteries, also known as primary cells, cannot reverse the chemical reaction after the discharge.
The discharge process is the same as that of a rechargeable battery. The redox reaction makes electrons flow from the anode to the cathode and power the external circuit. However, the battery is no longer usable when all electrons have reached the cathode terminal. For example, a non-rechargeable lithium battery is best for devices that need high energy density and a long shelf life. It can be used for immediate power needs, such as in flashlights, but is disposed of after full discharge.
Overall, two main factors decide the battery’s chargeability, i.e., electrode and electrolyte. The electrode material should support reversible chemical reactions in rechargeable batteries, like lithium-ion batteries. Similarly, electrolyte composition should support both forward and reverse reactions in rechargeable batteries.
Top 5 Differences Between Rechargeable and Non-Rechargeable Batteries
Now that the working principle is cleared. Let’s highlight the five differences between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries:
1. Electrolyte Composition
An electrolyte is a battery component that transfers ions between the anode and cathode terminals of the battery. There is a difference between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries regarding the electrolyte composition.
Rechargeable batteries use either alkaline or acidic electrolytes. For example, lithium-ion batteries use lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent, while lead-acid batteries use sulfuric acid as the electrolyte. The electrolyte composition is such that it can facilitate continuous charging and discharging cycles without degrading.
Non-rechargeable batteries use electrolytes for single-purpose use. For example, zinc-carbon batteries use a paste of zinc chloride or ammonium chloride, while alkaline batteries use potassium hydroxide. The filling electrolyte composition focuses on cost-effectiveness and stability.
2. Discharging Characteristics
Another difference between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries is discharging characteristics.
Rechargeable batteries are designed to support hundreds of charge and discharge cycles. Even when discharging, they provide stable voltage output and ensure consistent power supply.
Non-rechargeable batteries are designed for single use. You will witness full voltage output at the start and a gradual decrease in the voltage output as the battery discharges.
However, rechargeable batteries can do faster self-discharge than non-rechargeable batteries, which can hold the charge for a long time.
3. Environmental Impact
We cannot ignore the environmental impacts when discussing the differences between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries. Rechargeable batteries are more environmentally friendly because their long-term reuse reduces disposal rates and protects the environment. However, it is essential to recycle nickel, lithium, and cobalt properly when they are disposed of to minimize environmental harm.
In contrast, non-rechargeable batteries contribute significantly to environmental waste, as they are designed for one-time use and typically end up in the trash afterwards. Furthermore, if not disposed of properly, they can bring health risks to both humans and wildlife.
4. Emergency Situation
The difference between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries is also evident in emergency situations. Rechargeable batteries are less reliable in emergencies because they must be charged beforehand. As mentioned above, these batteries can self-discharge over time, so they are unreliable in emergencies. This is one of the main cons when considering the pros and cons of lithium batteries.
In contrast, non-rechargeable batteries can hold a charge for an extended period and can instantly fulfil power needs. Their ready-to-use nature makes them reliable during emergencies.
5. Hidden Danger
When looking at the differences between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries, we cannot ignore the hidden danger of both types.
Rechargeable batteries can be dangerous if not maintained properly. For example, overcharging, using the wrong charger, or exposure to high temperatures could lead to leakage or explosion. Similarly, non-rechargeable batteries can leak harmful chemicals if not well-maintained. These harmful chemicals can be hazardous to health and the environment.
How to Ensure Battery Safety When Manufacturing the Rechargeable Battery?
Rechargeable batteries require safety precautions not only during use but also during the manufacturing process. Below are some valuable tips to ensure battery safety during the lithium-ion battery manufacturing process:
- Use high-quality raw materials like pure lithium, cobalt, nickel, etc. This avoids impurities that can cause internal short circuits.
- Keep the manufacturing room clean to avoid contamination with dust and other elements.
- Keep the electrolyte composition stable and aligned with battery chemistry.
- Conduct electrical, mechanical, and thermal tests to ensure the battery meets safety standards.
- Provide employees with necessary safety training to follow safety protocols effectively.
- Use reliable manufacturing equipment to design highly accurate cells and automate the assembly process.
In short, safety measures are necessary to manufacture rechargeable batteries with reduced risks of common manufacturing hazards.
SZJ Automation’s Cylindrical Cell Turnkey Solutions – The Best Turnkey Solution to Manufacture Batteries
Now that the differences between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries are cleared, the next question is how to manufacture batteries in-house. That’s where SZJ Automation comes into action. We are a well-known name that provides ready-to-use turnkey solutions to manufacture rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries of different types.
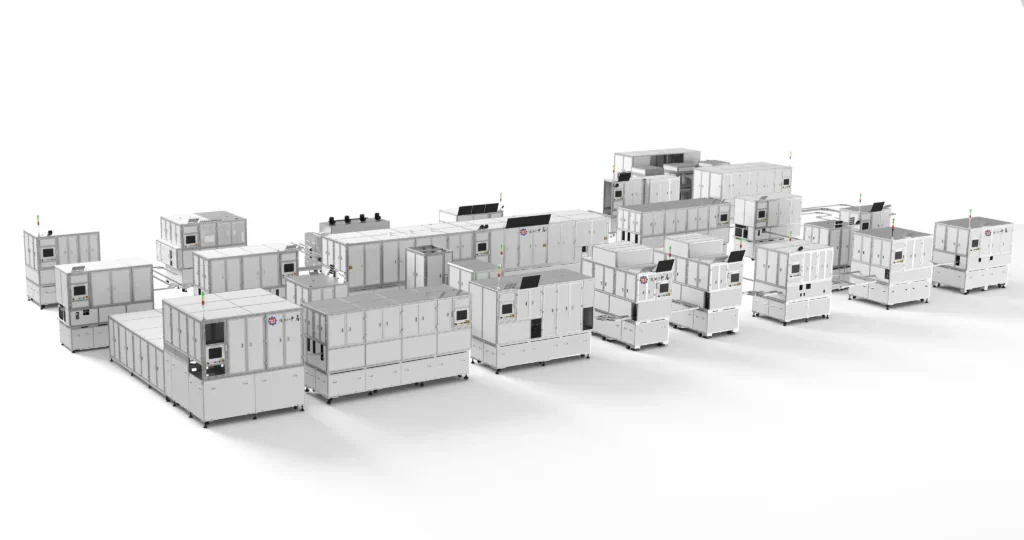
For example, our Cylindrical Cell Turnkey Solution can provide a complete production solution for turning raw materials into finished batteries. It offers all the core processes and equipment required for manufacturing batteries, such as an appearance inspection machine, automated cell insertion machine, grading machine, and more.
Besides, it supports a production rate ranging from 50 to 350 parts per minute (PPM), allowing manufacturers to scale operations efficiently to meet market demands. And our turnkey solution is designed to be flexible, accommodating both large and small cylindrical lithium and sodium batteries. This flexibility ensures that manufacturers can diversify their product lines and adapt to changes in battery size and chemistry without the need for significant retooling.
Conclusion
The differences between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries have shown that they differ on multiple elements, whether it’s electrolyte composition, discharge characteristics, or other factors. This makes them support different use cases.
When it comes to battery manufacturing, SZJ Automation dominates as a reliable partner because we have specialized in the intelligent equipment industry for over 20 years. If you are interested, please visit our SZJ Automation’s official websites to get more information and contact us!